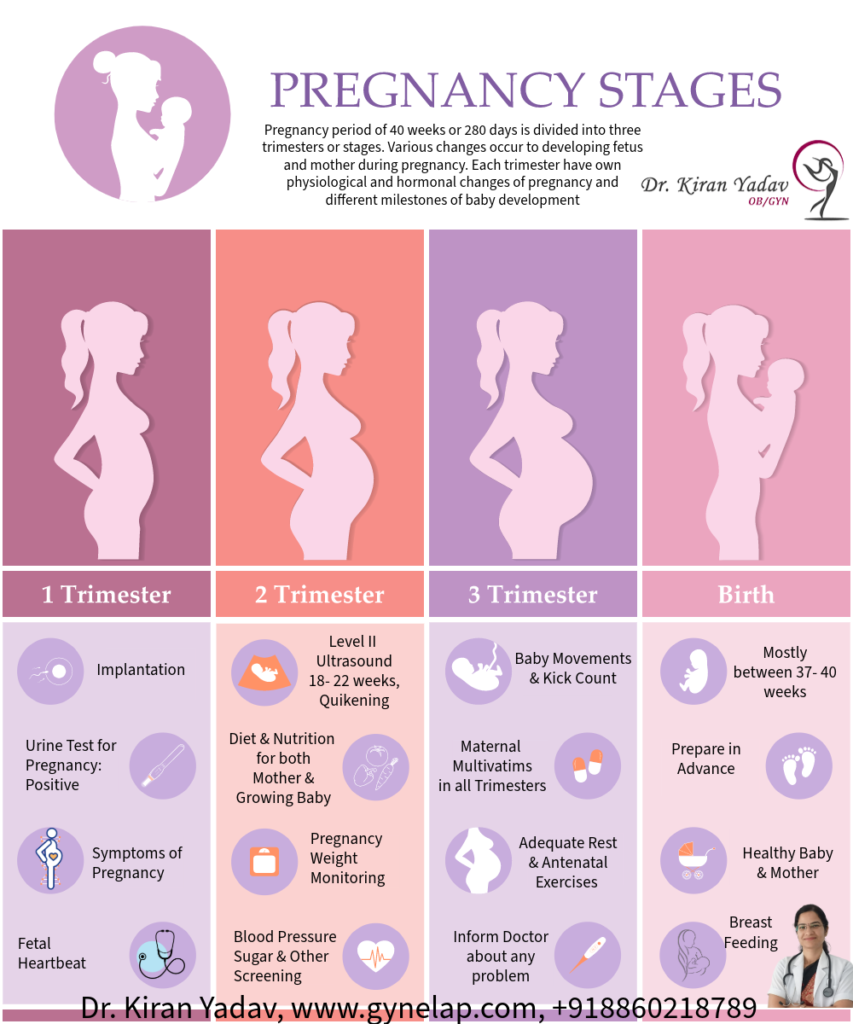
Stages/ Trimesters of Pregnancy
Pregnancy period of 40 weeks or 280 days is divided into three trimesters or stages. Various changes occur to developing fetus and mother during pregnancy. Each trimester has its own physiological and hormonal changes of pregnancy and different milestones of baby development. There are certain antenatal checkups and tests that are required to be done during each trimester of pregnancy for ensuring healthy and safe pregnancy.
First trimester of Pregnancy (weeks 1–12)
 The first trimester is the period from conception to 12 weeks of gestation. It is a time of rapid development for both mother and baby.
The first trimester is the period from conception to 12 weeks of gestation. It is a time of rapid development for both mother and baby.
Physiological changes during the first trimester of pregnancy:
- Missed period: This is usually the first sign of pregnancy for most women. Consult your doctor to confirm your pregnancy and estimate your due date.
- Breast changes: Increase in estrogen and progesterone hormones stimulate the development of the milk ducts and glands.
- Nausea and vomiting: Also known as morning sickness, this is one of the most common symptoms of early pregnancy. It can occur at any time of the day or night, and may be triggered by certain smells, foods, or movements. The exact cause of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy is not clear, but it may be related to the rising levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone, which is produced by the placenta. Morning sickness usually peaks around 9 weeks of pregnancy and subsides by the second trimester. To help relieve nausea and vomiting, you can try eating small, frequent meals; avoiding spicy, fatty, or greasy foods; drinking plenty of fluids; sucking on ginger candies or drinking ginger tea; and taking vitamin B6 supplements
- Mood swings: Mothers may experience a range of emotions during the first trimester of pregnancy, such as joy, anxiety, excitement, irritability, sadness, or fear. These are normal and are partly due to the hormonal changes.
- Fatigue: because body is working hard to provide nutrients and oxygen to the baby, as well as to produce more blood and hormones. Tahe rest during the day, adequate sleep, eat balanced diet, drink enough water, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol.
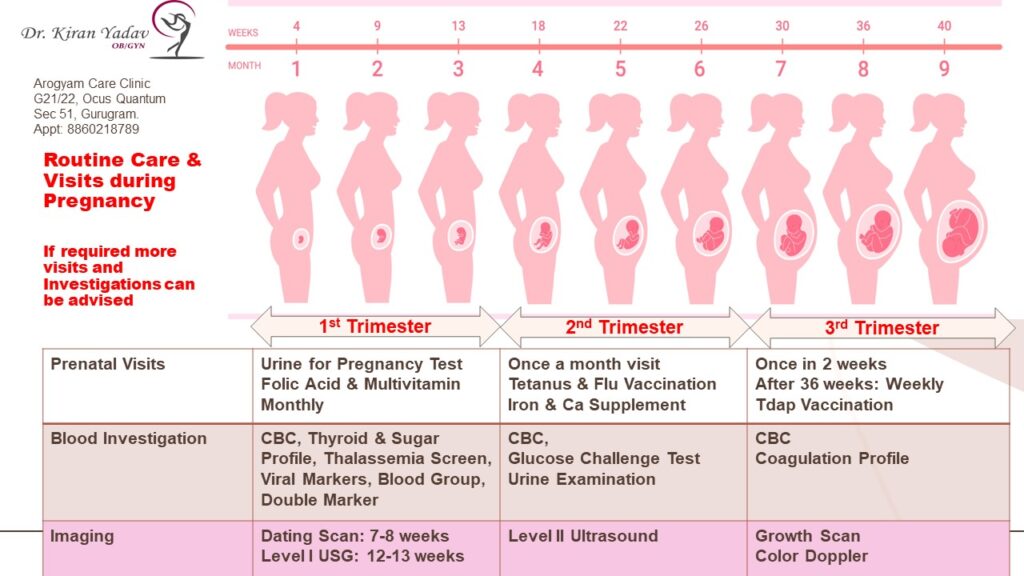
Antenatal Visit:
Your first prenatal visit will usually take place around week 8 of your pregnancy. This visit will involve:
- A detailed conversation about your medical history, family history, lifestyle, and any risk factors for pregnancy complications
- A physical exam, including a pelvic exam, measurement of weight, height, and blood pressure.
- Pregnancy test to confirm pregnancy.
- Blood test to check your blood type, Rh factor, hemoglobin level, and immunity to certain infections.
- The first heartbeat can be detected as early as the eighth pregnancy week.
- Urine test to check for signs of infection, protein, or sugar.
- Screening for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and HIV
- Ultrasound scan to determine your due date, the number of fetuses, the location of the placenta, and the fetal heartbeat.
- Blood test or a combined test (blood test and ultrasound) to screen for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome or Edwards syndrome
- Multivitamins and Folic acid started.
If the results of these tests are normal, you will likely have one prenatal visit per month until week 28 of your pregnancy. If the results are abnormal or you have other risk factors, you may need additional tests or more frequent visits.
Second trimester of Pregnancy (weeks 13–27)
Symptoms of first trimester usually decrease and chances of miscarriage decrease. Mothers feel more confident in sharing news with family.
Physiological Changes of Mother:
- Growing belly: As uterus expands to make room for the baby, your belly grows.
- Braxton Hicks contractions: may feel these mild, irregular contractions as a slight tightness in your abdomen. They’re more likely to occur in the afternoon or evening, after physical activity. Contact your health care provider if the contractions become regular and steadily increase in strength. This could be a sign of preterm labor.
- Skin changes: may develop brown patches on your face (melasma), dark line down your abdomen (linea nigra).
Baby Development milestones mainly includes:
- Quickening is baby first movement felt. It happens around 5th month
- Baby’s toenails develop
- Baby develops protective coating. Baby also has fine hair called lanugo that covers most of the body.
- Baby begins to hear and various organs develop
- 24 weeks onwards chances of survival outside womb increases.
Prenatal visits in the second trimester usually involve:
- Physical exam to check your weight, blood pressure, fundal height (the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus), and fetal heartbeat
- Flu & Tetanus Vaccination
- Urine test to check for signs of infection, protein, or sugar
- Blood test to measure your hemoglobin level and screen for gestational diabetes (usually between weeks 24 and 28)
- Level II ultrasound scan to assess your baby’s growth, anatomy, position, and amniotic fluid level (usually between weeks 18 and 22)
- Blood test or a quad screen (a combination of four blood tests) to screen for chromosomal abnormalities and neural tube defects (such as spina bifida or anencephaly)
If the results of these tests are normal, you will likely have one prenatal visit every two weeks until week 36 of your pregnancy. If the results are abnormal or you have other risk factors, you may need additional tests or more frequent visits.
Third trimester of Pregnancy (weeks 28 - 40)
The third trimester is the final stage of your pregnancy.
Physiological Changes :
- Weight gain: Expecting pregnant mothers may gain about 0.5 to 2 pounds per week in the third trimester. Too much or too little weight gain can increase the risk of some pregnancy complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or preterm birth.
- Swelling: third trimester mothers may experience some swelling in feet, ankles, hands, or face due to fluid retention and increased blood volume. This can be relieved by elevating your legs, wearing comfortable shoes, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding salty foods. However, if you have severe or sudden swelling or pain or warmth, you should consult your doctor.
- Backache or pelvic pain
Prenatal visits in the third trimester will usually involve:
- Physical exam to check your weight, blood pressure, fundal height, fetal heartbeat, and fetal position
- Urine test to check for signs of infection, protein, or sugar
- Blood test to check your hemoglobin level and screen for anemia
- Screening for Group B streptococcus (GBS), a common bacterium that can cause serious infections in newborns (usually between weeks 35 and 37)
- Cardiotocography (CTG) to monitor your baby’s heart rate and movements (usually in late pregnancy or during labor)
- Ultrasound scan to assess your baby’s growth, position, placenta location, and amniotic fluid level (if needed)
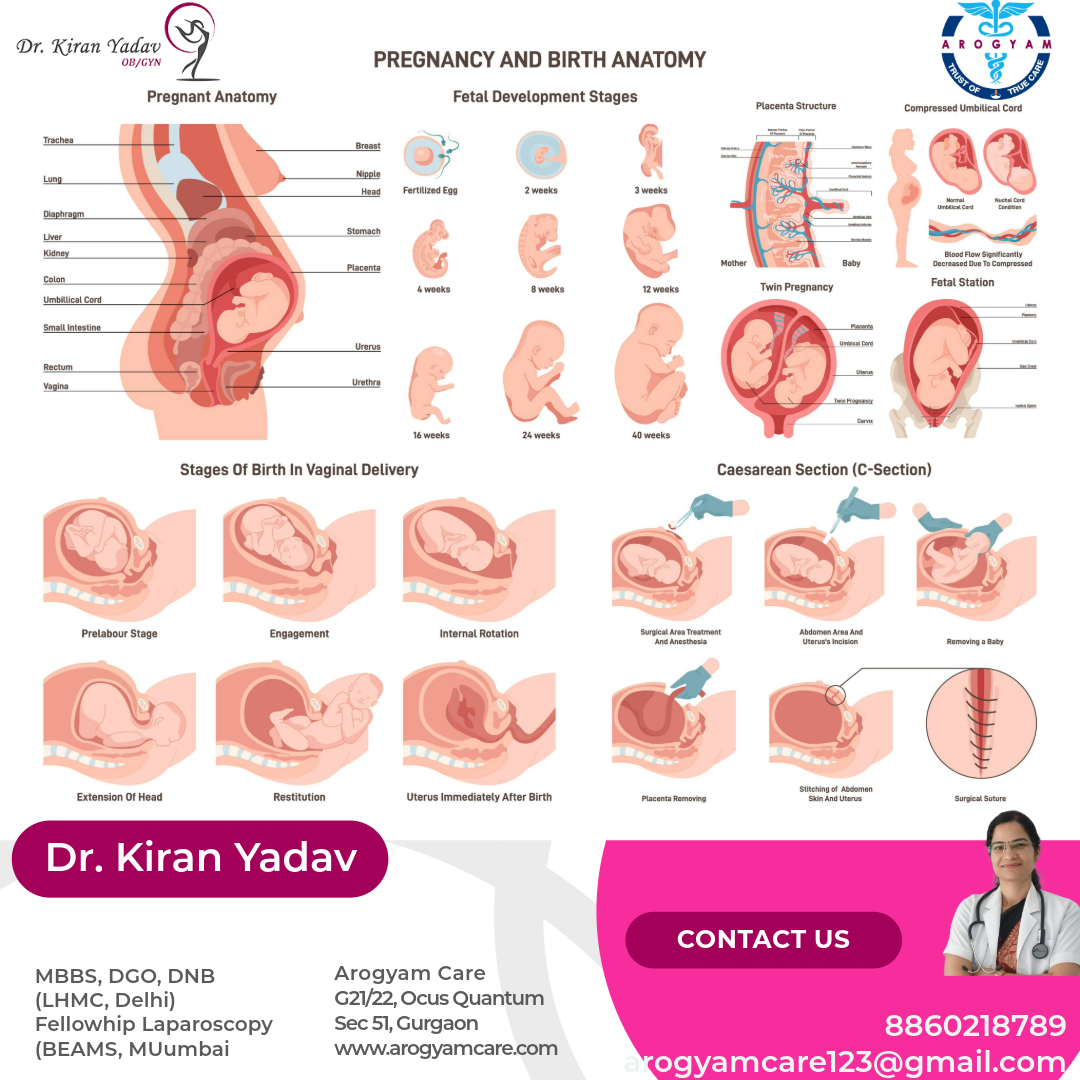
A “full term” pregnancy usually lasts between 39 weeks and 0 days to 40 weeks and 6 days. Normal delivery can take place between the 37th and 42nd weeks.