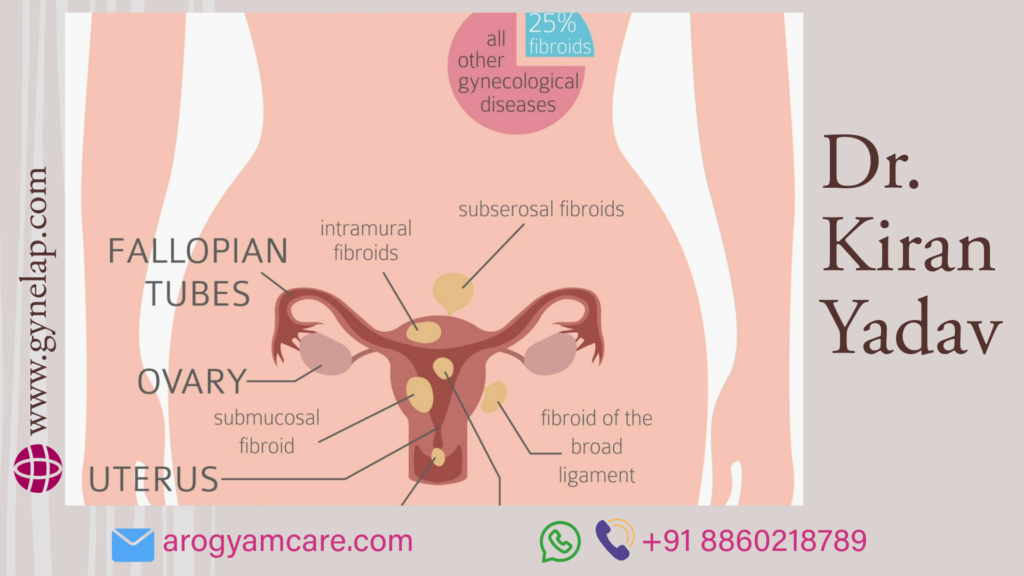
It is vital for every woman to care about her reproductive health. Uterus is shaped like a pear, but its shape keeps changing according to phase in a woman’s life. The most common ailment that afflicts the uterus is fibroid. Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus. They are also called leiomyomas or myomas. This affects women of childbearing age only. Many women may have it but not know until it is diagnosed.
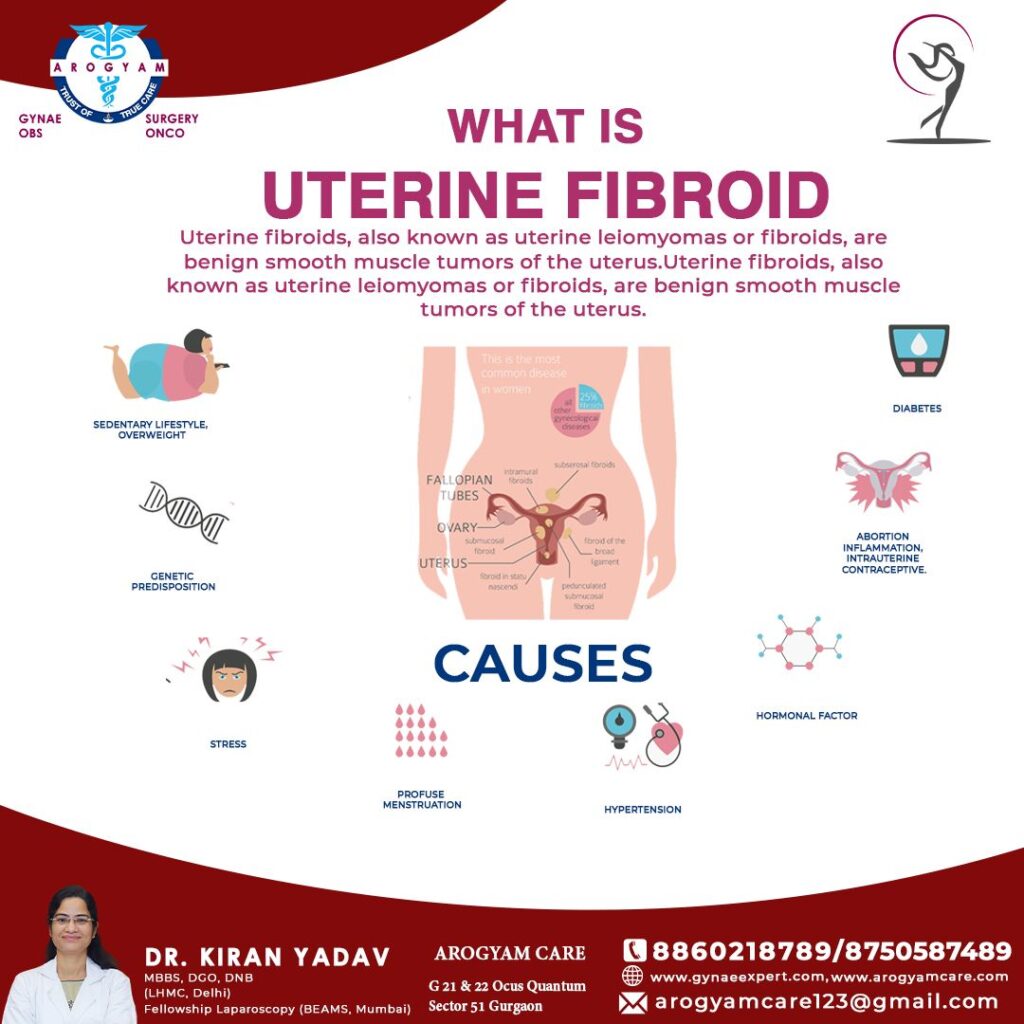
Cause of Fibroid:
- Age: more common in 30- 50 years.
- Race: more common and tend to be larger and more symptomatic in African.
- Family history
- Obesity: increase the estrogen levels and promote fibroid growth.
- Diet: high red meat and low fruits & vegetables increase the risk.
- Lifestyle: high blood pressure, diabetes, or an infection of the uterus
Symptoms of Fibroid
- Heavy menstrual bleeding: This may lead to anemia (low red blood cell count) and fatigue.
- Prolonged or irregular menstrual periods: This may cause inconvenience and discomfort.
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Backache or leg pain
- Backache
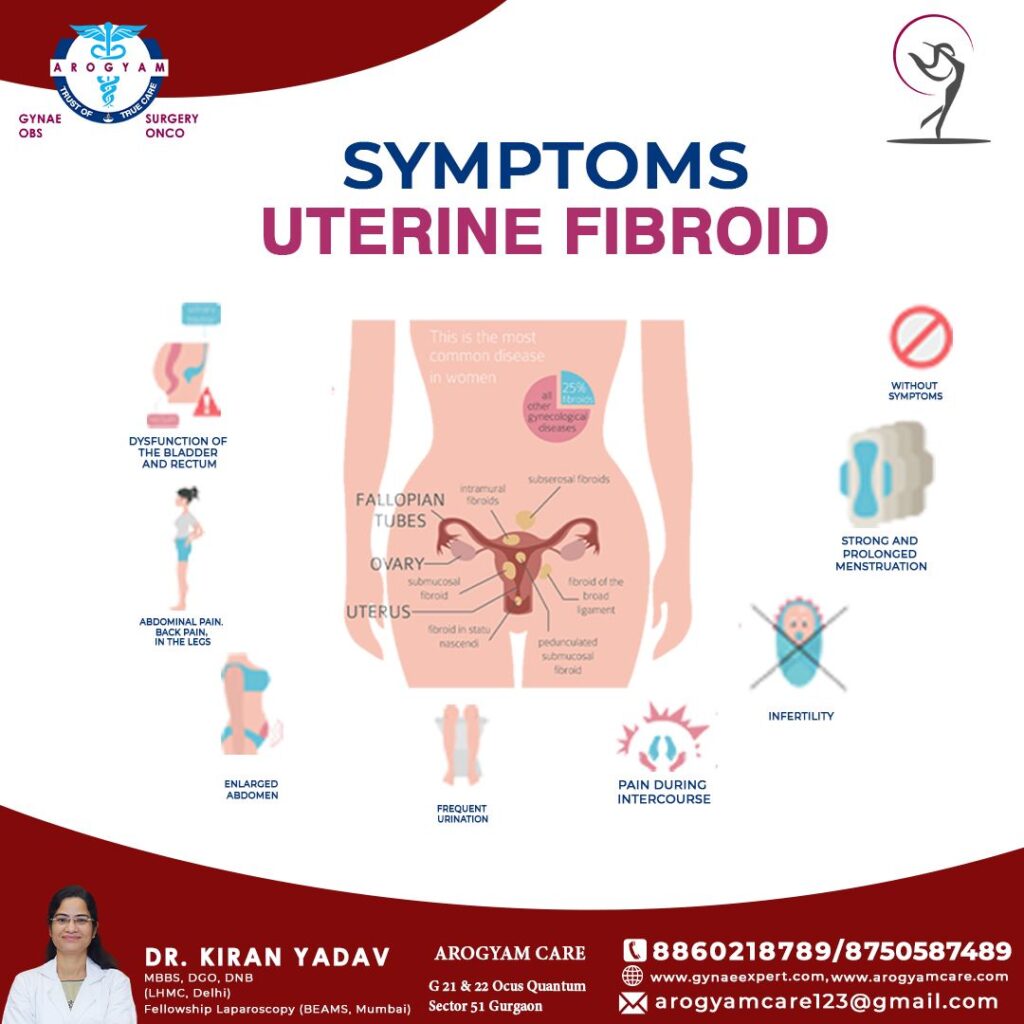
In some cases, uterine fibroids may cause complications such as:
- Infertility: because of distortion or blockage of the fallopian tubes.
- Miscarriage: because of reduced blood supply to the placenta or abnormal contractions of the uterus.
- Preterm labor: because of increased inflammation or infection in the uterus or premature rupture of membranes.
- Abnormal fetal position: This may happen because of reduced space in the uterus or malformation of the uterus.
- Cesarean delivery: This may be necessary because of obstruction by large fibroids or abnormal fetal position.
- Postpartum hemorrhage: This may happen because of poor contraction of the uterus after delivery or retained placenta.
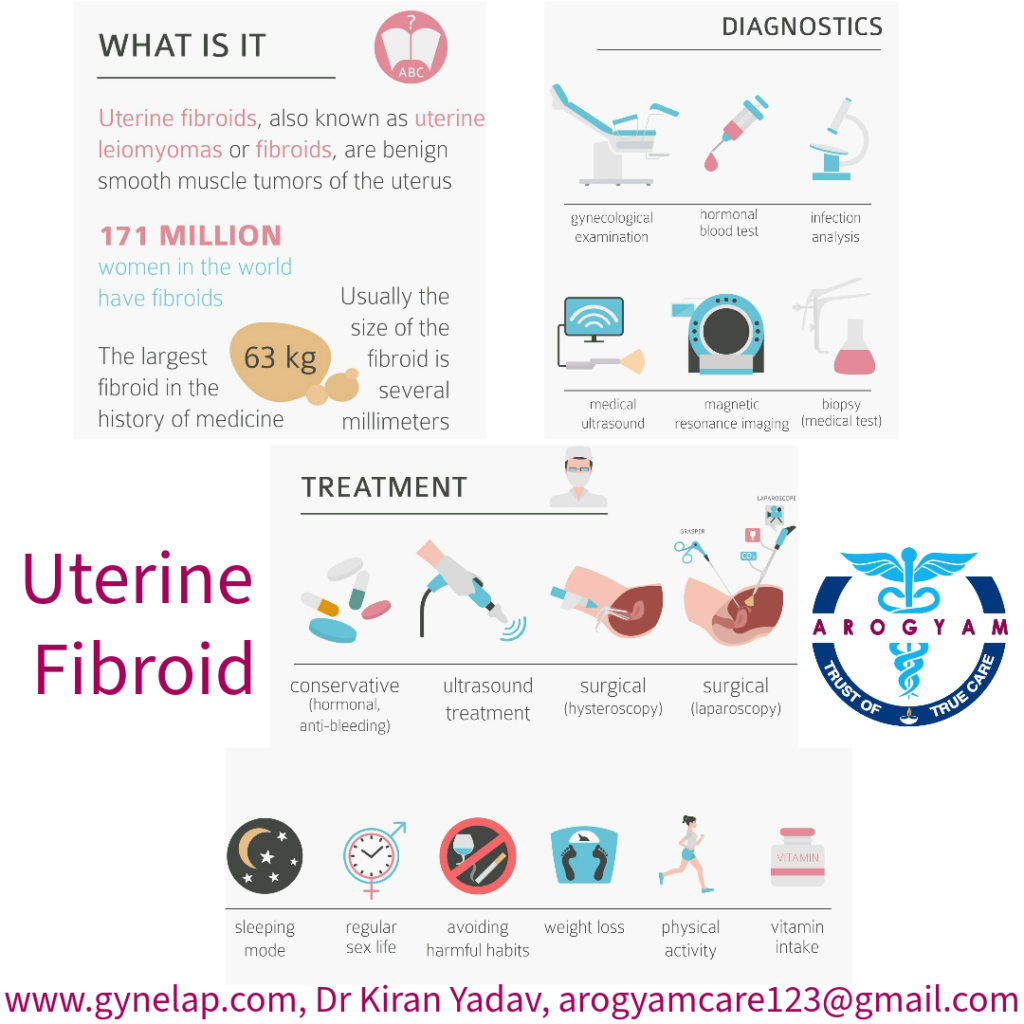
Investigations:
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in large and complex fibroids.
- Hysterosalpingography: It can help detect submucosal fibroids and blockage of the tubes.
- Hysteroscopy: This is a procedure that uses a thin, lighted telescope (hysteroscope) to look inside the uterus. It can help diagnose and treat submucosal fibroids and other problems of the uterine lining.
Treatment
Observation- most of the asympotomatic fibroids- do not need any treatment, just observation and Ultrasound every 6 months or yearly.
– Levonorgestral IUD or Mirena – The use of Mirena can lessen symptoms like heavy bleeding. Although it may not lessen the size of fibroid.
Medical methods- GnRH agonists- they induces temporary menopause like phase, as a result menstruation stops, fibroids shrink and anaemia improves.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy- according to the type of fibroids- if the fibroid is located inside the uterine cavity, it can be treated by hysteroscopy . Hence no cut on abdomen and fast recovery.
Laparoscopic surgery- This comes into picture when no medication works. In this fibroid is removed fully. A surgeon removes it by viewing the fibroid on the screen. This is beneficial as recovery time is quicker than a traditional surgery.
Abdominal myomectomy- sometimes depending upon size and MRI findings doctor can suggest open or traditional surgery too.
Fibroid doesn’t mean you are not normal. One just needs a good treatment