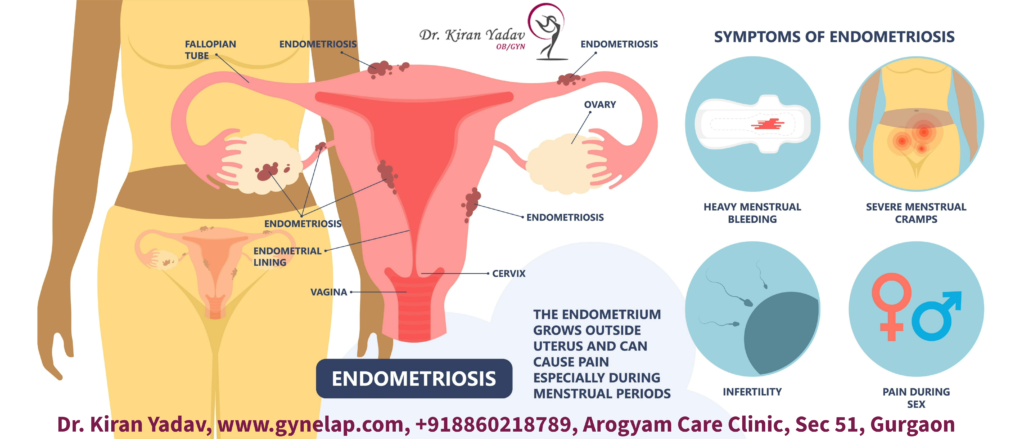
What is endometriosis?
According to best gynecologist in Delhi NCR, endometriosis is a common condition, and it affects every 1 in 10 women of reproductive age. It occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, usually on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic wall, bladder, bowel, or other organs. This tissue responds to hormonal changes and bleeds during menstrual cycles, causing inflammation, pain, and scar tissue formation. Endometriosis can also interfere with fertility and quality of life.
Causes of endometriosis: why endometriosis occurs?
The exact cause of endometriosis is not known, but several factors ca contribute to its development as best gynae doctors in Gurgaon. These include:
- Retrograde menstruation: This is when some of the menstrual blood and tissue flows backward through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvic cavity, where it implants and grows.
- Genetic factors: Endometriosis tends to run in families and may be influenced by certain genes that affect hormone levels or immune system function.
- Immune system dysfunction: Some women with endometriosis may have an impaired immune system that fails to recognize and eliminate the abnormal tissue growths.
- Hormonal imbalance: Endometriosis is dependent on estrogen, a hormone that stimulates the growth of the endometrium and the endometriotic lesions. Women with high levels of estrogen or low levels of progesterone may be more prone to endometriosis.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins that mimic estrogen or disrupt hormone balance may increase the risk of endometriosis.
Symptoms of endometriosis:
- The main symptom of endometriosis is pelvic pain, especially during periods, sex, bowel movements, or urination. The pain can range from mild to severe and may vary from person to person.
- Some women may also experience heavy or irregular bleeding.
- fatigue
- bloating, nausea, or diarrhea.
- Some women with endometriosis may have no symptoms at all and only discover they have the condition when they have trouble getting pregnant.
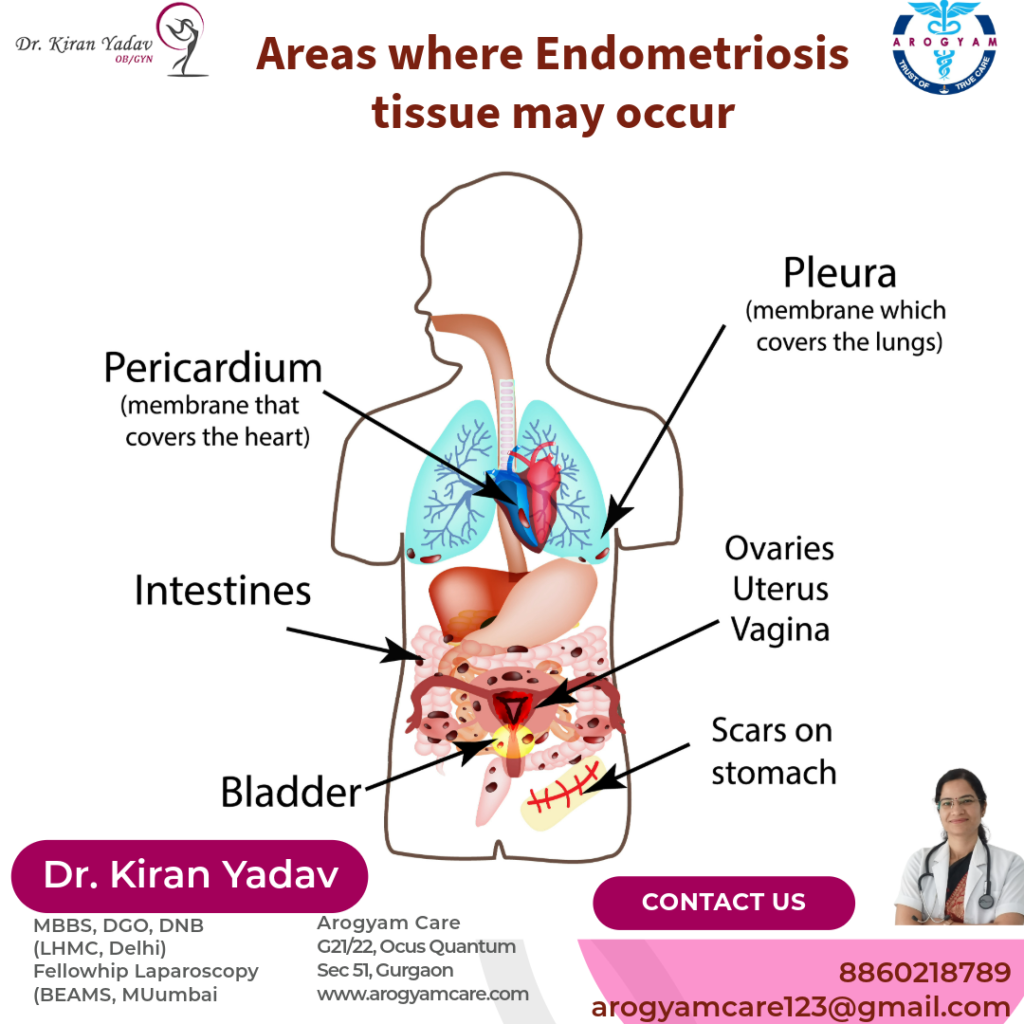
Sites/organs where endometriosis can develop
Sites where endometriosis can develop includes outside and back of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, vagina, peritoneum (the lining of your abdomen and pelvis), urinary bladder, ureters, Intestine. Rarely it can develop in scar, pericardium and pleura.
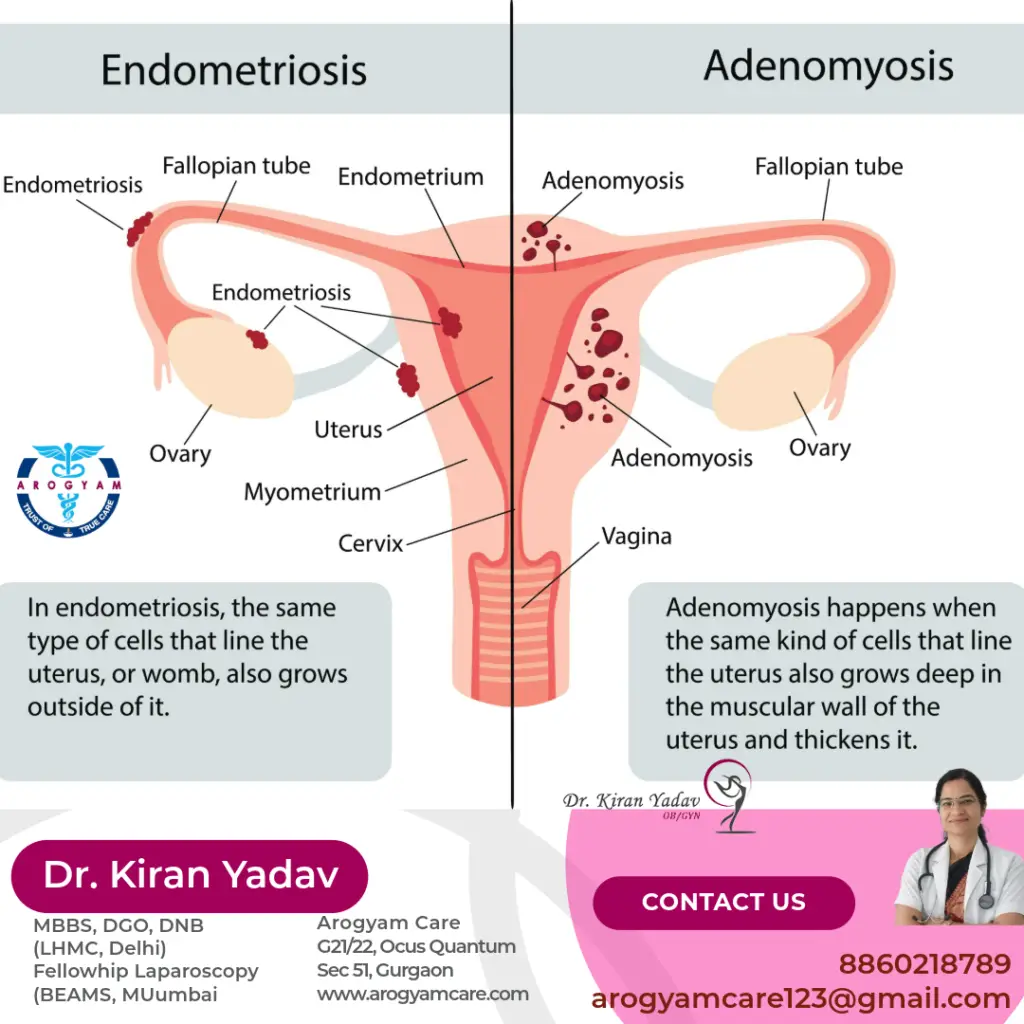
What is adenomyosis?
Difference between endometriosis and adenomyosis: Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that lines the inner layer of uterus (endometrium) grows into the wall of the uterus.
Investigations for endometriosis:
The diagnosis of endometriosis is based on a combination of:
- medical history
- physical examination
- imaging tests (such as ultrasound or MRI)
- laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a thin tube with a camera and light (laparoscope) through a small incision in the abdomen to view the pelvic organs and confirm the presence and extent of endometriosis. Laparoscopy by laparoscopic gynaecologist can also be used to treat endometriosis by removing or destroying the abnormal tissue.
Treatment of Endometriosis:
The endometriosis treatment options depends on several factors, such as the severity of symptoms, the location and size of lesions, the age and reproductive plans of the woman, and her personal preferences. The main goals of treatment are to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, prevent or treat infertility, and improve quality of life. The treatment options for endometriosis includes:
Medical Treatment:
- painkillers (such as ibuprofen or naproxen)
- hormonal contraceptives (such as pills, patches, rings, or injections)
- progestins (such as medroxyprogesterone acetate or levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device),
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists (such as leuprolide or goserelin)
- aromatase inhibitors (such as letrozole or anastrozole)
- anti-inflammatory drugs (such as celecoxib)
These medications work by reducing pain, inflammation, bleeding, and hormone levels that stimulate endometriosis growth. However, they may have side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, bone loss, hot flashes, vaginal dryness, or decreased libido.
Surgery for endometriosis:
- Endometriosis Surgery: Removing or destroying the endometriotic lesions using laparoscopy or laparotomy (a larger incision in the abdomen).
- Surgery can provide long-term relief from pain and improve fertility outcomes.
- Surgery may have side effects such as infection, bleeding, organ damage, adhesions (scar tissue that binds organs together), or recurrence of endometriosis.
Supportive therapies: These include dietary changes, exercise, stress management techniques. Endometriosis diet recommendations includes :
- Fiber: Increase intake (35g/day) from fruits, veggies, flaxseed, and legumes.
- Omega-3 Fats: Include fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
- Avoid Red Meat.
- Avoid Processed Foods.
- Moderate Alcohol and Caffeine.
- Soy: May help regulate estrogen.

