Gynecological Health: Importance, Key Areas, and Preventive Care
Gynecological health refers to the overall well-being of a woman’s reproductive system, which includes the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. Maintaining good gynecological health is essential for women of all ages, as it plays a critical role in overall health, fertility, sexual function, and disease prevention. Regular check-ups, early detection of issues, and preventive measures are crucial to managing and maintaining reproductive health.
1. Why Gynecological Health Is Important
Gynecological health is central to a woman’s physical and emotional well-being. It affects multiple aspects of life, from menstruation and sexual activity to fertility and menopause. Ignoring signs of gynecological issues can lead to complications such as infertility, chronic pain, and even life-threatening conditions like cancer. Regular care ensures that potential problems are detected early and treated effectively.
2. Key Areas of Gynecological Health
Gynecological health encompasses a wide range of issues and conditions, each requiring appropriate care and attention. The key areas include:
A. Menstruation
Menstruation is a key indicator of reproductive health. Women can experience a range of issues related to their menstrual cycle, such as:
- Irregular Periods: These can indicate hormonal imbalances, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or thyroid problems.
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Also known as menorrhagia, this can be caused by uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or hormonal imbalances.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD): Both conditions can affect mood, physical health, and daily activities in the days leading up to menstruation.
B. Contraception and Family Planning
Choosing the right contraceptive method is an essential part of gynecological care. Options range from hormonal methods (such as birth control pills, implants, and IUDs) to permanent solutions like tubal ligation. Counseling on contraception helps women plan their families and manage reproductive health more effectively.
C. Pregnancy and Fertility
Gynecological health is directly linked to fertility and pregnancy. Women seeking to conceive or prevent pregnancy benefit from regular check-ups, preconception counseling, and fertility evaluations. Common issues affecting fertility include:
- Endometriosis: A condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside it, causing pain and potentially affecting fertility.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can cause irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and infertility.
- Ovulation Problems: Irregular ovulation can lead to difficulty conceiving and is often caused by hormonal imbalances.
D. Gynecological Cancers
Several types of cancer affect the reproductive system, including:
- Cervical Cancer: Often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), cervical cancer is preventable with regular Pap smears and HPV vaccination.
- Ovarian Cancer: This cancer can be difficult to detect early and often presents with symptoms like bloating, pelvic pain, or difficulty eating.
- Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer: Often associated with abnormal uterine bleeding, endometrial cancer is more common in postmenopausal women.
E. Menopause
Menopause marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years, typically occurring in the late 40s or early 50s. It can bring significant changes to physical and emotional health. Common symptoms include hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. Post-menopausal women also face an increased risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease, making preventive care essential during this stage of life.
F. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Gynecological health also involves preventing and managing STIs, which can impact fertility and overall well-being. Regular screening for STIs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HPV is important, especially for sexually active women.
3. Preventive Care for Gynecological Health
Preventive care is crucial for maintaining long-term gynecological health and detecting issues before they become severe. The key components of preventive care include:
A. Regular Gynecological Exams
Regular visits to a gynecologist help identify potential issues early. These exams typically include:
- Pap Smears: A Pap smear is a screening test for cervical cancer. Women should begin getting Pap smears at age 21 and continue with regular screenings as recommended by their healthcare provider.
- Pelvic Exams: A pelvic exam checks the health of the reproductive organs and is often performed during routine check-ups.
- HPV Testing: The HPV vaccine can prevent cervical cancer, and regular testing for HPV is recommended, especially for women aged 30 and older.
B. Vaccinations
The HPV vaccine is an important preventive measure for cervical cancer. It is most effective when given before a woman becomes sexually active, but can still benefit those who are sexually active.
C. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact gynecological health. Recommendations include:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and can help prevent issues like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps regulate hormones and maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for reproductive health.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are linked to several gynecological issues, including cervical cancer and infertility.
D. Sexual Health and Protection
Safe sex practices, including the use of condoms and regular STI testing, are essential to prevent infections that can affect reproductive health. Open communication with a healthcare provider about sexual health is important for addressing any concerns or risks.
4. Common Gynecological Health Issues
Several common gynecological conditions affect women’s health. These include:
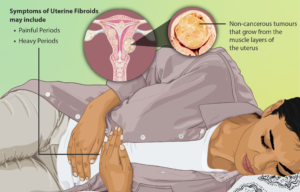
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding and pain. Treatment options vary from medication to surgery, depending on the severity.
- Endometriosis: A painful condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to chronic pain and potential fertility issues.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries, which may resolve on their own or require surgical intervention.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal imbalance that affects ovulation, menstrual cycles, and fertility.
5. Mental and Emotional Aspects of Gynecological Health
Gynecological health isn’t just about physical well-being. The emotional and psychological aspects of reproductive health are equally important. Many women face challenges such as anxiety, depression, or body image concerns related to their gynecological health. Conditions like infertility, painful periods, or menopause can have a profound emotional impact. Seeking emotional support, whether through counseling, support groups, or therapy, can be beneficial for overall well-being.
Conclusion
Gynecological health is an essential aspect of a woman’s overall health. Regular exams, preventive care, and attention to symptoms can help women maintain reproductive health throughout their lives. By understanding the common conditions, screening guidelines, and lifestyle choices that impact gynecological health, women can take proactive steps to safeguard their well-being and lead healthier lives. Prioritizing regular check-ups and seeking professional care when needed are vital steps in ensuring long-term health and fertility.