Ovarian Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
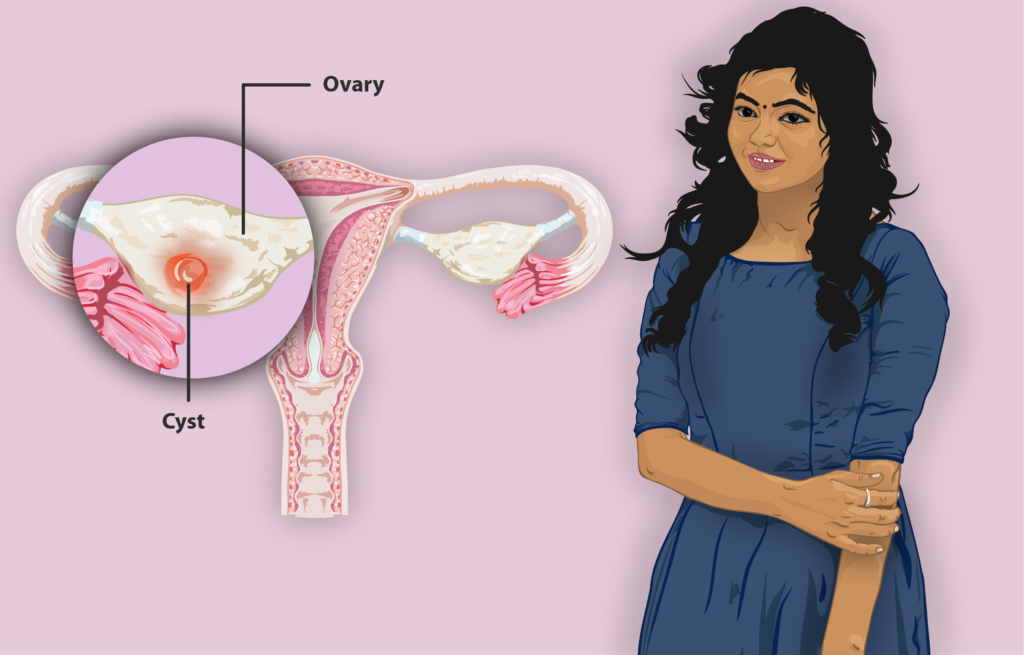
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside a woman’s ovaries. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own without medical intervention. However, some cysts can cause discomfort, complications, or even require surgical treatment. Understanding the different types of ovarian cysts, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for women’s reproductive health.
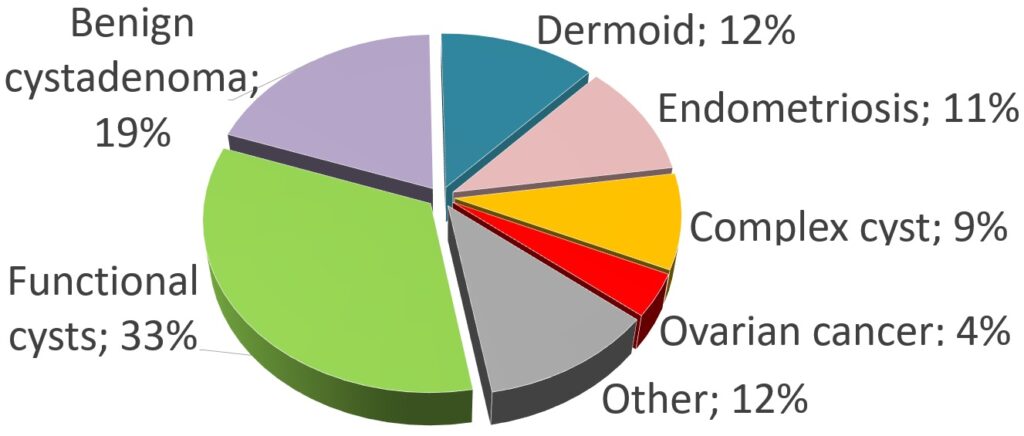
Types of Ovarian Cysts
- Functional Cysts: These are the most common type of ovarian cysts and often form as a normal part of the menstrual cycle. They include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts.
- Pathological Cysts: These cysts result from abnormal cell growth and can include dermoid cysts, endometriomas, tumors, cystadenomas.
Causes:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can contribute to cyst formation.
- Endometriosis: can lead to endometriomas.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Age: reproductive age functional cysts common, older age pathologic cysts common
- History of Ovarian Cysts
- Family History: A family history of cysts
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
- Asymptomatic and detected incidentally on imaging like ultrasound.
- Pelvic Pain: Dull, aching pain in the lower abdomen
- Bloating or Fullness of abdomen.
- Irregular Periods
- Pain During Intercourse
- Frequent Urination
- Sudden, Severe Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: May indicate a ruptured or twisted cyst.
- Fever and Vomiting: Signs of infection or a ruptured cyst.
- Faintness or Dizziness: May result from internal bleeding.
Invesyigations for Ovarian Cysts
- Pelvic Examination
- Ultrasound
- Blood Tests: S. CA-125, HE 4,S. AFP, beta hCG, LDH are tumor markers useful in some cases.
- MRI or CT Scan: These may be used for further evaluation if needed.
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy: When there is doubt rgarding nature of ovarian cyst, it better to assess directly by laparoscopy and if required it is removed and histologic analysis done.
Biopsy/ FNAC is NOT done in case of Ovarian cyst/ Lesion.
Treatment of Ovarian cyst:
Treatment Depends on Several Factors:
- Size and Type of Cyst: Small, functional cysts may resolve on their own. Larger or complex cysts may require treatment.
- Symptoms: Treatment may be recommended if pain or other symptoms.
- Age and Reproductive Plans: age and desire for future pregnancies influence treatment decisions.
Common Treatment Options:
- Watchful Waiting:** Monitoring the cyst’s growth with regular follow-up.
- Medications: Hormonal contraceptives or medication to induce ovulation.
- Surgery: In cases of large or persistent cysts, laparoscopic surgery may be recommended to remove the cyst while preserving the ovary.
Ovarian cysts are a common occurrence among women and can vary in size and type. While most cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some may require medical attention and treatment. If you experience symptoms or have concerns about ovarian cysts, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance tailored to your specific situation. Early detection and appropriate management can help ensure your overall gynecological health and well-being of life.
Prevention of Ovarian Cysts
While it’s not always possible to prevent ovarian cysts, certain steps may reduce the risk of developing them:
Regular Pelvic Exams: Regular check-ups help detect ovarian cysts early and monitor their growth.
Birth Control Pills: Hormonal contraceptives may prevent the formation of new cysts by regulating ovulation.
Managing Endometriosis and PCOS: For women with conditions like endometriosis or PCOS, managing these underlying health issues can help reduce the likelihood of developing cysts.
Ovarian Cysts and Fertility
In most cases, ovarian cysts do not affect fertility, especially if they are functional cysts that resolve on their own. However, certain types of cysts, such as those related to endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may interfere with fertility. Surgery to remove cysts can also pose a risk to fertility if part of the ovary needs to be removed. Women who are concerned about their fertility should discuss this with their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological condition that most women will experience at some point in their lives. While most cysts are benign and resolve on their own, others can cause symptoms or complications that require medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help women manage their reproductive health and seek timely care when needed. Regular pelvic exams, paying attention to symptoms, and seeking medical advice when necessary are essential for maintaining ovarian health.