PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease)/ PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome):
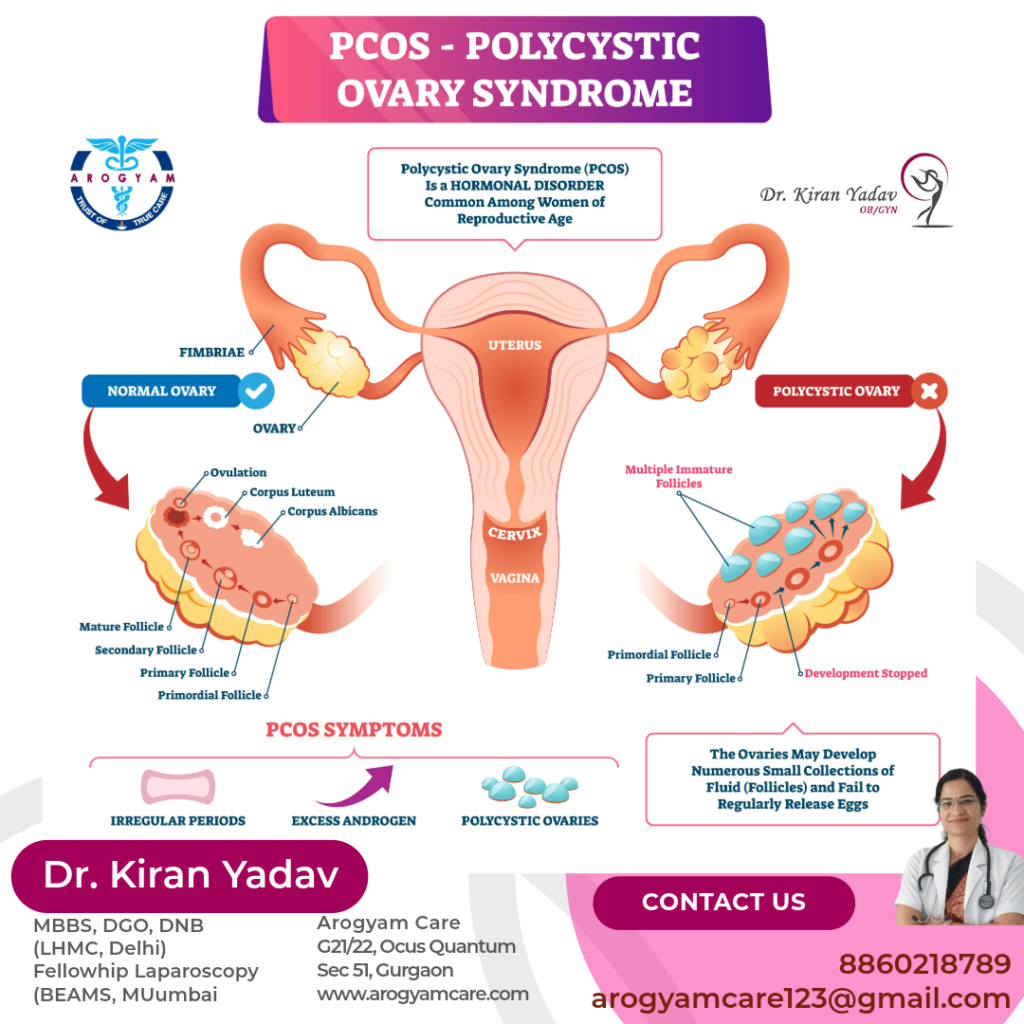
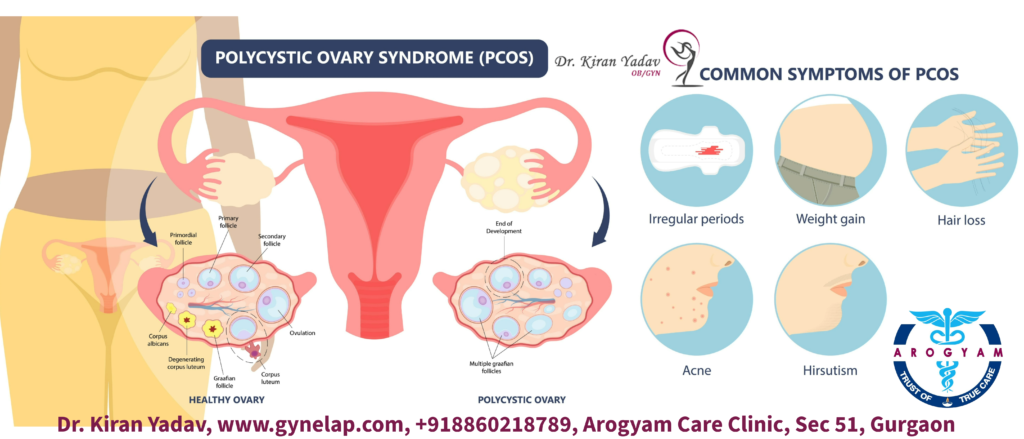
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) are common hormonal disorders affecting 8-13% of women of the reproductive age. These conditions can significantly impact a woman’s health, leading to various symptoms and complications. This blog post explores how PDOD and PCOS affect women’s health, available treatment options, and essential self-care practices.
Symptoms of PCOS and PDOD
- Irregular Periods: Women with PCOD often experience irregular menstrual cycles, which can include missed periods or very heavy bleeding.
- Excessive Hair Growth: This condition can cause hirsutism, which is excessive hair growth on the face, chest, and back.
- Acne: Due to hormonal imbalances, women with PCOD may suffer from severe acne.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOD experience weight gain and have difficulty losing weight.
- Thinning Hair: Hair thinning or male-pattern baldness can occur.
- Darkening of skin (acanthosis nigricans)
- Infertility: PCOD can lead to difficulties in conceiving due to irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation.
- Mood Changes: Women with PCOD may experience mood swings, depression, and anxiety.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and low energy levels are common.
Health Implications/ Complications of PCOD
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) can lead to several complications and long-term health implications if not managed properly.
- Infertility: One of the most significant complications of PCOD is infertility. The hormonal imbalance can interfere with ovulation, making it difficult for women to conceive.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Women with PCOD are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: PCOD can increase the risk of heart diseases due to associated conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity
- Endometrial Cancer: The irregular menstrual cycles associated with PCOD can lead to a thickened endometrium, increasing the risk of endometrial cancer by 2.7 times in patients of PCOD.
- Obesity: Many women with PCOD struggle with weight gain and obesity, which can exacerbate other health issues.
- Sleep Apnea: Obesity and hormonal imbalances can contribute to sleep apnea, a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Stress: PCOD can lead to mood swings, depression, and anxiety due to hormonal changes and the stress of dealing with the symptoms.
Treatment of PCOD
Treating Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) as suggest by PCOS specialist doctor; involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical procedures. Here’s a detailed look at the various treatment options:
- Lifestyle Changes
1. Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can be a helpful PCOD/ PCOS diet to manage symptoms. Regular physical activity can also improve insulin sensitivity and help with weight management.
2. Weight Loss: Even a modest reduction in weight (5-10% of total body weight) can significantly improve symptoms and increase the effectiveness of medications. - Medications
1. Birth Control Pills: These helps regulate menstrual cycles, reduce male hormone levels, and clear acne.
2. Anti-Androgens: Medications like spironolactone can reduce excessive hair growth and acne by lowering androgen levels.
3. Metformin: This medication improves insulin resistance and can help with weight loss and menstrual regularity.
4. Fertility Medications: Clomiphene citrate and letrozole are often used to stimulate ovulation in women who are trying to conceive. - Surgical Options
1. Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling: This procedure involves making small holes in the ovaries to restore normal ovulation. It’s usually considered when other treatments haven’t worked.
Self-Care Treatments Options for PCOD/ Alteranate treatment options for PCOD
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a nutritious diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Adequate Sleep: try to maintain a bedtime routine and avoid electronic devices before sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep.
- Stress Reduction: Practice stress-relief techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation. Enjoyable activities, games and practicing self-care rituals can also help reduce stress.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Stay hydrated with lot of water and avoid high sugary drinks
- Support Networks: Join support groups or connect with others who have PCOS or PDOD for emotional support and advice.
- Supplements: Some women find relief with supplements like inositol, which can improve insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance.
- Regular Monitoring and Medical Check-Ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider are essential to monitor symptoms and adjust treatments as needed